Atomic Structure
Exploring the atomic world
Element:
Elements are pure and simple substances consisting of one type of atom.
For example: Sodium (Na), Magnesium (Mg), Uranium (U), Bromine (Br).
Compound:
Compounds are pure substances as well, consisting more than one types of atoms bonded together.
For example: NaCl (Sodium Chloride), CaCo3 (Calcium Carbonate), HCl (Hydrogen Chloride)
Mixture:
Mixtures are two or more different kinds of substances that are not chemically combined together.
Atomic number:
The atomic number is the total number of protons in the nucleus of an atom.
Mass/Nucleon number:
Mass/Nucleon number refers to the total number of protons and neutrons in the nucleus of an atom.
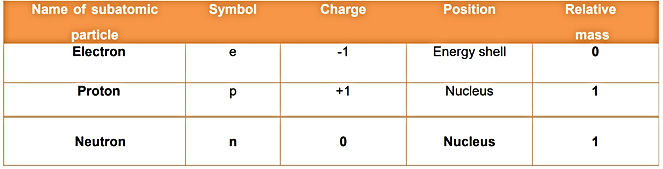
Subatomic particles:
Electrons, Protons and neutrons are called subatomic particles.
Ions
-
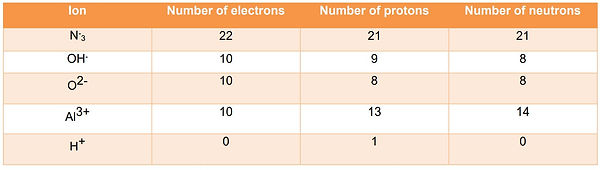
Ions have unequal number of protons and electrons.
-
Ions are formed due to the loss and gain of electron.
Ions can be identified in two respects:
Cations:
-
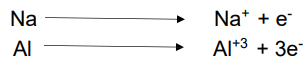
Positively charged ions are called Cations
-
Cations are formed due to the loss of electron.
-
Cations have more protons than electrons.
-
Number of charges on the cations indicates the number of electrons donated.
For example:
Anions:
-
Negatively charged ions are called Anions.
-
Anions are formed due to gain of electrons.
-
Anions have more electrons than protons.
-
Number of negative charges on the Anions indicate the number of electrons taken.
For example:

Isotopes
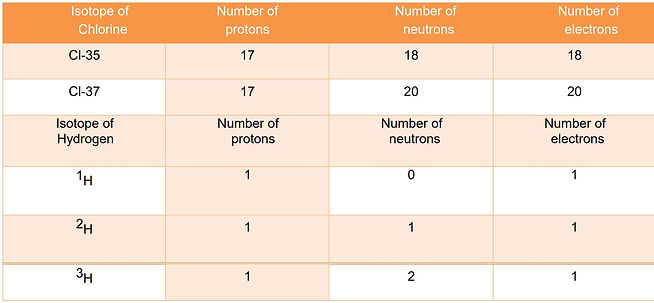
Isotopes are the atoms of the same element that have same number of protons but different number of neutrons.
Isotopes have same:
-
number of protons
-
atomic radius
-
electronic configuration
-
Similar chemical properties
On the other hand
Isotopes have different:
-
number of neutrons
-
nucleon number
-
physical properties
-
relative isotopic mass
-
mass number
Points to remember!
Electronic configuration of an atom is the arrangement of electrons in different energy shells of an atom.
n = number of energy shell.
Maximum number of electrons in an energy shell = 2n2

-
The number of electrons present in the outermost shell of an atom represents the group number.
-
The number of energy shells of an atom represents the period number.
-
Metallic elements (group 1,2,3) donate electrons.
-
Non-metallic elements (4,5,6,7) gain electrons.
