Nucleotide: A nucleotide is a molecule consisting of a nitrogenous base, a pentose sugar, and a phosphate group. Nitrogen-containing base can be : 1. Purine - double ring structure.
2. Pyrimidine - single ring structure. /////////mamu diagram 1////// *phosphate group attached to pentose sugar by ester bond, the phosphate group is negatively charged *nitrogen base is attached to pentose sugar by a glycosidic bond. In DNA pentose sugar is deoxyribose. In RNA, ATP pentose sugar is ribose. There are 5 nitrogen bases 1. Adenine [A] (Purine - double ring structure ). 2. Guanine [G] (Purine - double ring structure ). 3. Cytosine [C] (Pyrimidine - single ring structure). *Cytosine is not found in RNA. 4. Thymine [T] (Pyrimidine - single ring structure). 5. Uracil [U] (Pyrimidine - single ring structure). *Uracil is not found in DNA.
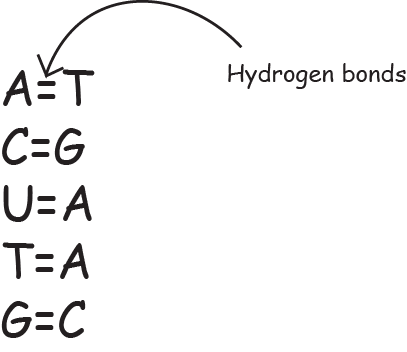
There are 2 hydrogen bonds between A and T, A and U and 3 hydrogen bonds between C and G. Complementary base pairing occurs between purines and pyrimidines. A always binds with T / U by 2 hydrogen bonds. G always binds with C by 3 hydrogen bonds. Polynucleotide A polynucleotide is polymerized by forming bonds between the carbon of pentose sugar and an oxygen atom of phosphate. \\\\\mamu diagram 2 ///// A polynucleotide has a free phosphate group at end-1 and a free OH group at end-2. \\\\\\mamu diagram 3 including the labels on it pleaseeeeee :P ///// Nucleic acid Nucleic acids are DNA and RNA which are polymers of many nucleotides. DNA : DNA is a polynucleic acid that carries genetic information in cells and is capable of self-replication and synthesis of RNA. DNA is a 3D molecule \\\\\\mmau diagram 4 ///// Structure of DNA DNA is double-stranded, there is 2 polynucleotide strand. The two strands are wound around each other to form a double-helix
The polynucleotide strands are joined together by hydrogen bonds between complementary bases, these bases form base pairs (A and T or C and G).
Base pairs are specific, A only binds with T, C only with G. These are called complementary base pairs, this means whatever the sequence of bases along the strand, the sequence of bases on the other strand must be complementary to it. Erwin Chargaff's findings, Proportion of A equal to the proportion of T and
The proportion of G is equal to the proportion of C . Explanation of how Chargaff's findings helped Watson and Crick work out the structure of DNA. 1. Complementary base pairing, A with T and C with G.
2.Purines bind with pyrimidines.
3.There is hydrogen bonds between base pairs so distance between strands of DNA are equal and strands run antiparallel. How the structure of proteins made scientists think that these were molecules that carried information .......
Proteins being made from a sequence of amino acids and different proteins having different sequences of amino acids let scientists to believe that proteins carried information.
Function of DNA
DNA is the genetic material made of genes.
Function of DNA is to replicate with all its genes and be copied during each cell division.
Genes on DNA control the characteristics of a cell.
Structural features of DNA that makes it a stable molecule :
-Complementary base pairing between purines and pyrimidines holds the strands together because of many hydrogen bonds between them.
Significance of DNA being very stable -Sequence of nucleotides will not spontaneously change, so chances of mutation are decreased.
-Proteins that is produced from the code of DNA will always be functional. -Stability of DNA maintains all genetic information throughout the life of cell.
Importance of hydrogen bonding in DNA structure:
-Hydrogen bond holds two polynucleotides together.e
-Many hydrogen bonds give stability, so strands are not easily separated.
-Individual hydrogen bonds are more easily broken than covalent bonds, so strands can be separated for replication or transcription .
-Hydrogen bonds only form between specific based so few mistakes during hence replication will be exact.
-Hydrogen bonds is important in contribution to 3-D structure of DNA molecule.
Gene Definition : Gene is a length of DNA that codes for a particular polypeptide /protein.
Gene Code The sequence of bases in DNA of a cell is the code for all the proteins of that cell and organism.
Gene Mutation
Definition : Gene mutation is the change in nucleotide sequence of DNA resulting in formation of polypeptide with altered function.
Genetic Code
The three base sequence in the coding strand which codes for an amino acid is called the genetic code, e.g. TAC, the genetic code for amino acid methionine. ////mamu diagram 5 \\\
Features of genetic code:
-Genetic code is 3 letter code, known as triplet, this means that 3 bases make the code for 1 amino acid, e.g. TAC, the genetic code for amino acid methionine.
-Genetic code is universal, meaning that each triplet codes for the same amino acdis in all living organism.
-Genetic code has punctuation, 3 of the DNA triplet act as full stops. ATT , ATG and ACT , on mRNA it is UAA UAC UGA. During protein synthesis these stop triplets marks the end of a gene. ///////////////mamu diagram 6//////////
*Methionine has ONLY ONE codon , AUG .
-Genetic code is redundant or degenerate, which means that more than one triplet specifies an amino acid, e.g. amino acid Cystein is coded by ACA or ACG, the third letter can be A or G so the code for Cystein is AC purine, since A and G are purine.
-There are 61 codons for 20 amino acids and 3 stop codons.
Mutation
A mutation is a spontaneous change in : 1. Structure of DNA (Gene mutation). 2. Structure or number of chromosomes (Chromosome mutation).
Gene mutation : - Gene mutation is a change in the nucleotide sequence in a length of a DNA that leads to the formation of a non-functional polypeptides or altered polypeptides. Chromosome mutation : -Chromosome mutation is a spontaneous change in the structure or number of chromosomes in a cell.
Mutation can be caused by :
-Error during DNA replication
-Mutagens, e.g. ionizing radiation, UV light, X-ray, tar in tobacco smoke, asbestos, benzene etc.
-Virus: Human papillomavirus.
The main reason for mutation is cancer.
Comentários